colour_visuals.VisualRGBColourspace3D#
- class colour_visuals.VisualRGBColourspace3D(colourspace: RGB_Colourspace | str | Sequence[RGB_Colourspace | LiteralRGBColourspace | str] = 'sRGB', model: LiteralColourspaceModel | str = 'CIE xyY', colours: ArrayLike | None = None, opacity: float = 1, material: Type[gfx.MeshAbstractMaterial] = gfx.MeshBasicMaterial, wireframe: bool = False, segments: int = 16)[source]#
Bases:
MeshCreate a 3D RGB colourspace volume visual.
- Parameters:
colourspace (RGB_Colourspace | str | Sequence[RGB_Colourspace | LiteralRGBColourspace | str]) – RGB colourspace to plot the gamut of.
colourspaceselements can be of any type or form supported by thecolour.plotting.common.filter_RGB_colourspaces()definition.model (LiteralColourspaceModel | str) – Colourspace model, see
colour.COLOURSPACE_MODELSattribute for the list of supported colourspace models.colours (ArrayLike | None) – Colours of the visual, if None, the colours are computed from the visual geometry.
opacity (float) – Opacity of the visual.
thickness – Thickness of the visual lines.
material (Type[gfx.MeshAbstractMaterial]) – Material used to surface the visual geomeetry.
wireframe (bool) – Whether to render the visual as a wireframe, i.e., only render edges.
segments (int) – Edge segments count for the RGB colourspace cube.
Examples
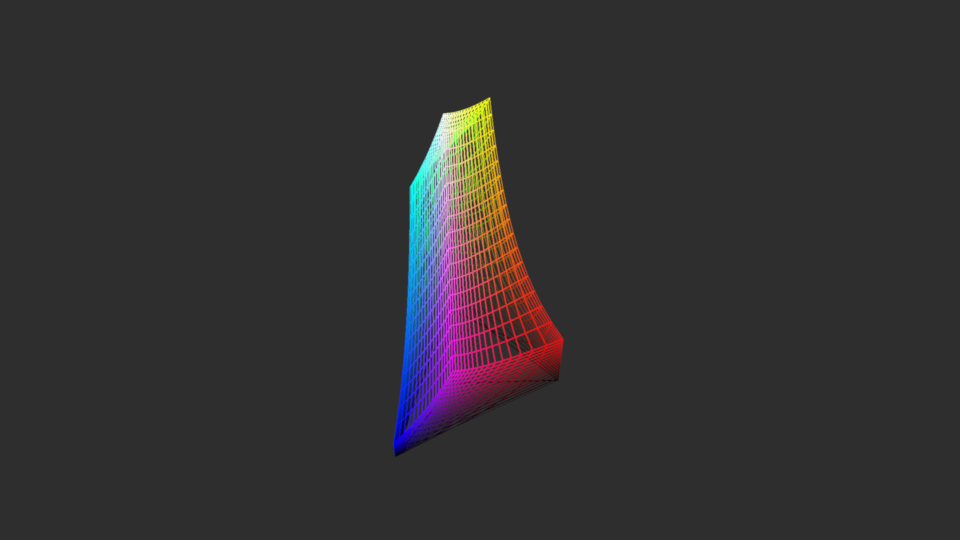
>>> import os >>> import pylinalg as la >>> from colour.utilities import suppress_stdout >>> from wgpu.gui.auto import WgpuCanvas >>> with suppress_stdout(): ... canvas = WgpuCanvas(size=(960, 540)) ... scene = gfx.Scene() ... scene.add( ... gfx.Background( ... None, gfx.BackgroundMaterial(np.array([0.18, 0.18, 0.18])) ... ) ... ) ... visual = VisualRGBColourspace3D(wireframe=True) ... visual.local.rotation = la.quat_from_euler( ... (-np.pi / 4, 0), order="XY" ... ) ... camera = gfx.PerspectiveCamera(50, 16 / 9) ... camera.show_object(visual, up=np.array([0, 0, 1]), scale=1.25) ... scene.add(visual) ... if os.environ.get("CI") is None: ... gfx.show(scene, camera=camera, canvas=canvas) ...
- __init__(colourspace: RGB_Colourspace | str | Sequence[RGB_Colourspace | LiteralRGBColourspace | str] = 'sRGB', model: LiteralColourspaceModel | str = 'CIE xyY', colours: ArrayLike | None = None, opacity: float = 1, material: Type[gfx.MeshAbstractMaterial] = gfx.MeshBasicMaterial, wireframe: bool = False, segments: int = 16)[source]#